Recognition of Prior Learning and Higher Education often use words or terminology that can be quite daunting to a newcomer. These words can also often vary across institutions and countries. The following terms are those most frequently used when we refer to RPL in a Higher Education.
Access
Process by which applicants enter a programme of study. RPL can be used as a mechanism to secure admission to a programme where the applicant does not meet the standard entry criteria.
Transfer
Process by which a student can transfer from one programme to another by being awarded general credit (no grades associated with the credit) to recognise learning outcomes already achieved in the previous programme. All transfers at Maynooth University are managed through the central Admissions Office.
Progression
Progression refers to how a student, upon successful completion of a year or programme, can respectively progress to the subsequent year or another programme.
Module
A module is a self-contained unit of a student's workload. Modules are typically delivered and assessed within a semester. A ‘module descriptor’ is available to students for all modules. The module descriptor sets out what the objectives and learning outcomes of the module are, how many credits attach to the modules, how it will be assessed etc.
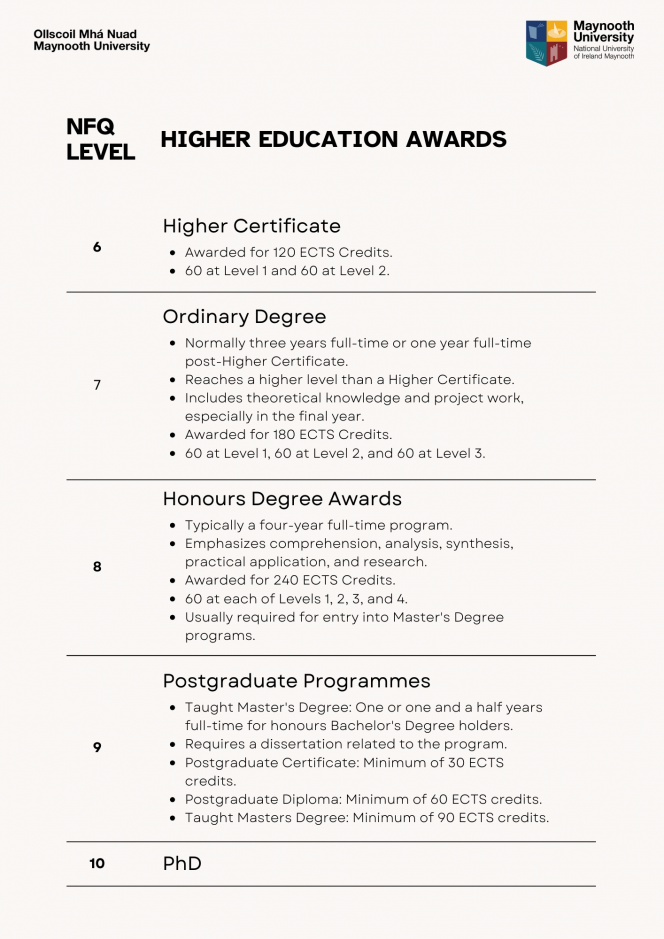
National Framework of Qualifications (NFQ)
The NFQ is a ten-level system of education and training awards standards. The fan diagram depicts the levels on the NFQ, awarding bodies and major types of qualifications.
Programme (or Course)
The terms ‘Programme’ and ‘Course’ are used interchangeably at Maynooth University and refer to the overall title of what you are studying e.g. BSc (Bachelor of Science) of Economics
Formal Learning
Formal Learning refers to certified learning in a programme which has learning outcomes against which learning can be assessed, credited and can result in a recognised award.
Non-Formal Learning
Non-Formal Learning occurs through planned learning activities which are often not certified and do not result in academic credit (e.g. Online learning, short extramural courses)
Informal Learning
Informal Learning or ‘experiential’ learning refers to the knowledge, skills and competencies that an individual attains through life and work experiences.
Accreditation of Prior Learning (APL)
APL is simply another term for Recognition of Prior learning (RPL) and refers to how an individuals prior learning is identified, assessed and recognised for the purpose of developing their formal education
Recognition of Prior Experiential Learning (RPEL)
RPEL refers to informal learning acquired through experience such as the learning we acquire through our home, working and voluntary life activities. This is often also referred to as Accreditation of Prior Experiential Learning (APEL)
Recognition of Prior Certified Learning (RPCL )
RPCL refers to formal learning that has been undertaken in recognised universities, colleges/institutes and awarding bodies. This is often referred to as Accreditation of Prior Certified Learning (APCL)
ECTS Credits & the National Framework
The Irish National Framework of Qualifications (NFQ) is a 10-level system used to describe qualifications in the Irish education and training system. It describes what learners need to know, understand and be able to do to achieve a qualification. When an RPL applicant submits formal learning as part of their applicaiton to Maynooth University, we take that learning and map it to the framework to ascertain your highest level of education.
Higher education awards, which are awards which occur following secondary education in Ireland, are classed into a number of groups as shown in the followin graphic: